
Space Medicine
The Issue of Aging in Space
Spaceflight presents immensely difficult challenges. Weightlessness, partial gravity, planetary dust, and space radiation pose a significant threat to humans in both spaceflight and living in planetary habitats, which can result in the rapid development of life-threatening diseases in astronauts. In addition, the closed environments can create additional stress on a space crew's work performance and mental wellbeing.
The word “weightlessness” is used in this report to describe the condition that astronauts experience in different locations of altered gravity during the space flights. The term ‘’microgravity” has it’s limitations as it is basically means one millionth of the Earth gravity and it is incorrect to apply to the conditions that astronauts undergo during the space missions. Advancements in Longevity are crucial for the future of space exploration. As more private companies continue to expand the space economy, the viability of space-Longevity research substantially increases.


Investors in the Space Medicine Industry

More than half (around 74%) of investors in Space Medicine are in the United States. An additional 14% of investors are located in Europe, including 4% each in the UK and Germany, 3% each in Finland and Switzerland. Also 3% of investors are based in Singapore. Other investors are spread worldwide.
Most Advanced Space Medicine Companies

60% of companies shown have their headquarters in the U.S., with Israel, France and Switzerland sharing second place (30% of all private companies). Other companies are distributed equally among the UK, Netherlands and Italy.
Services to Enhance Space Medicine Industry

25% of the marketplace is dedicated to bioengineering solutions for astronauts to adverse age-related degenerative conditions: eye and bone implants, or medical hardware to analyse and support astronauts’ health.
Another 25% of the space medical market is focused on the biotechnology industry dealing with space-related disorders and in situ amino-acid production.
More than 35% of space-related companies provide research equipment for the ISS.
5% are dedicated directly to human longevity in space. In particular, a new venture-capital fund called SP8CEVC has been established to place a laser-tight focus on the intersection between space technology and human longevity.
Private Age-Related Research in Space
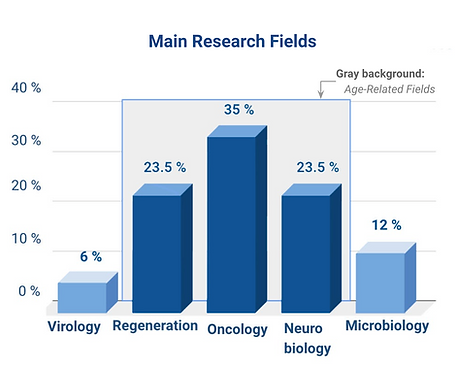
Low-Earth orbit (LEO) is a unique environment for investigation of novel approaches to mitigate age-related disorders.
35% of all private research on the ISS dedicated to drug-delivery systems to conquer cancer.
Another 47% of applied sciences are equally focused on neurodegenerative disorders therapy, mainly Alzheimer’s, and regenerative medicine: muscle and bone restoration, using human-cell culture.
As microbes in space change their metabolism, and cause serious harm to astronauts, almost 12% of private research is dedicated to microbiology and 6% to viral replication and production studies, including the development of vaccines for space.
Cost of Private Research on the ISS has Increased since 2019
In April 2021 after discussions with stakeholders about the current market growth, and in anticipation of future commercial entities capable of providing similar services, the new NASA commercial marketing pricing policy was formed and prices went up significantly.


Growing Interest in Private Research in Space Medicine
Today, more and more space startups are arising and promoting private research in space. Giving the current rising interest, commercial research is increasingly taking over the market.
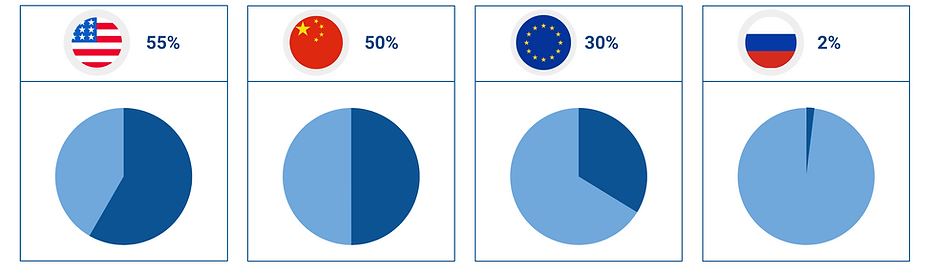
55% of the U.S. SpaceTech market is coming from the private sector. The second country by the number of private space initiatives is China with half of the market dedicated to commercial R&D. The European Union holds third place with 30% of the space projects initiated by private companies. Though historically Russia has the most experience in space research, space commercialisation only began there in 2018. Since then only one Russian company has carried out private research in space - 3D Bioprinting Solutions.
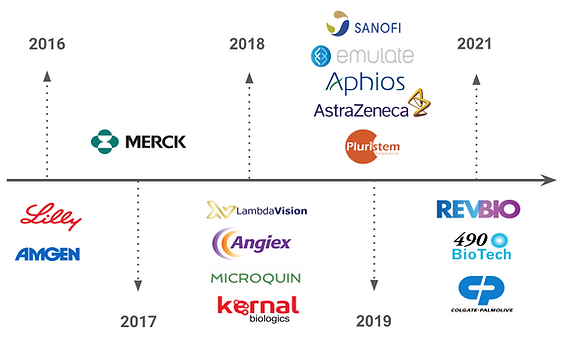
Timeline of Private Biological Research on the International Space Station
ISS became available to private companies beginning in 2016.
Most of the investigations were carried out by pharmacological companies and were related to pharmacokinetics and drug delivery systems.
Due to the pandemic, no private research was carried out in 2020.
Biomanufacturing in Space - Main Sectors
The Biomanufacturing is one of the most prominent and fast-growing industry Space Medicine Solutions. Most of the technologies that are being produced in space are used on Earth, proposing the set of unique approaches that are not possible without wheightlessness.

Leading positions in biomanufacturing are devoted to regenerative medicine which covers 23% of the industry, and organ printing (3D bioprinting) with 22.4% of the global market.
The third place is occupied by drug discovery and drug development using the protein crystallisation technique. with 11.6 percent of the market in each sector. 7.2% is focused on the aging process in bones, muscles, and brains under spaceflight conditions.
Cell therapy, including stem cells, has occupied 6.3% of biomanufacturing research. 13% is almost equally distributed among the organs-on-chips approach, medical devices, and research equipment for the ISS. Statistics include both private and governmental initiatives.
Space Medicine Framework
The Physiological Changes in Astronauts
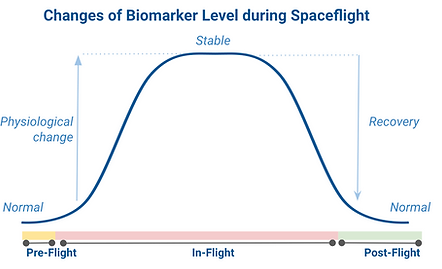
Astronauts enter orbit in perfect health, but during spaceflight, their bodies undergo physiological changes.
These changes stabilize during their stay in space, but a transformation occurs again when they return to Earth.
The astronauts then need to undergo rehabilitation before recovering to their initial, stable condition. Space-medical researchers can observe and examine this entire process over short periods of time.
Even with the rehabilitation process, some post-flight health conditions are still observed.

Orbital Space Missions with Human Presence

The graph represents the maximum attitudes of crewed space missions. Most of the experiments presented in this report were performed on the International Space Station with approximately 90% of the Earth's gravity and radiation ranging from 12 to 28.8 Gy per day.
TRL of Space Travel-Related Biomarkers
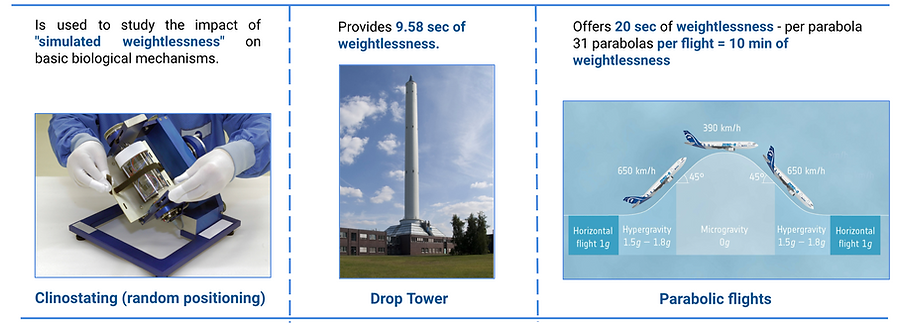
All of the following approaches allow the validation of experiments before travelling to the International Space Station (ISS). While clinostating is used for only mimicking the effects of weightlessness, drop-tower and parabolic flights create short-term weightlessness on Earth affordable for life sciences-experiments, especially in vitro cultures and research on mice. Suborbital flights will soon allow several minutes. Most experiments with humans are currently being done in parabolic flights and space medical research is carried out on the ISS specifically.
Study Investigates How Men and Women Adapt Differently to Spaceflight
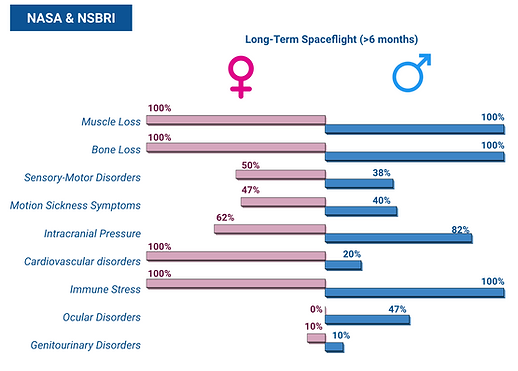
This diagram shows key differences between men and womens physiological adaptation to the spaceflight environment.
This includes:
-
Cardiovascular,
-
Immunological,
-
Sensorimotor,
-
Musculoskeletal, and
Behavioral alterations etc.
Radiation Resistance


